Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens
| CD59 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1CDQ, 1CDR, 1CDS, 1ERG, 1ERH, 2J8B, 2OFS, 2UWR, 2UX2, 4BIK |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | CD59, 16.3A5, 1F5, EJ16, EJ30, EL32, G344, HRF-20, HRF20, MAC-IP, MACIF, MEM43, MIC11, MIN1, MIN2, MIN3, MIRL, MSK21, p18-20, CD59 molecule, CD59 molecule (CD59 blood group) |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 107271; MGI: 1888996; HomoloGene: 56386; GeneCards: CD59; OMA:CD59 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 11p13 | Start | 33,703,010 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 33,736,479 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 2|2 E2 | Start | 103,900,194 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 103,921,532 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - stromal cell of endometrium
- bronchial epithelial cell
- right lung
- olfactory zone of nasal mucosa
- gallbladder
- upper lobe of left lung
- minor salivary glands
- tibial nerve
- smooth muscle tissue
- spinal ganglia
|
| | Top expressed in | - brown adipose tissue
- spermatid
- choroid plexus
- bone marrow
- choroid plexus of fourth ventricle
- right kidney
- epiblast
- morula
- quadriceps femoris muscle
- liver
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 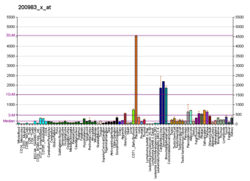

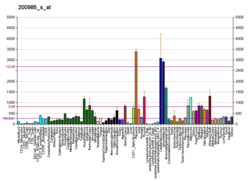 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein binding
- complement binding
| | Cellular component | - vesicle
- endoplasmic reticulum membrane
- membrane
- focal adhesion
- Golgi membrane
- plasma membrane
- extracellular region
- cell surface
- compact myelin
- anchored component of external side of plasma membrane
- ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane
- anchored component of membrane
- sarcolemma
- extracellular exosome
- endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane
- extracellular space
- specific granule membrane
- tertiary granule membrane
- transport vesicle
| | Biological process | - blood coagulation
- negative regulation of apoptotic process
- negative regulation of activation of membrane attack complex
- endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport
- cell surface receptor signaling pathway
- COPII vesicle coating
- positive regulation of T cell proliferation
- regulation of complement activation
- cell activation
- neutrophil degranulation
- regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_203331
NM_000611
NM_001127223
NM_001127225
NM_001127226
|
|---|
NM_001127227
NM_203329
NM_203330 |
| |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000602
NP_001120695
NP_001120697
NP_001120698
NP_001120699
|
|---|
NP_976074
NP_976075
NP_976076
NP_000602.1
NP_001120695.1
NP_001120697.1
NP_001120698.1
NP_001120699.1
NP_976074.1
NP_976075.1
NP_976076.1 |
| |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 11: 33.7 – 33.74 Mb | Chr 2: 103.9 – 103.92 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
CD59 glycoprotein, also known as MAC-inhibitory protein (MAC-IP), membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (MIRL), or protectin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD59 gene.[5] It is an LU domain and belongs to the LY6/uPAR/alpha-neurotoxin protein family.[6]
CD59 attaches to host cells via a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. Cholesterol-containing microdomains aid in CD59 activity by stimulating a "pinch point" in the lipid membrane during MAC assembly to prevent pore-formation and inhibit lysing.[7] When complement activation leads to deposition of C5b678 on host cells, CD59 can prevent C9 from polymerizing and forming the complement membrane attack complex.[8] It may also signal the cell to perform active measures such as endocytosis of the CD59-C9 complex.[6] Endocytosis of this complex leads to the destruction of the ion channel formation that this complex provides to the MAC. These ion channels are used for transfer of different ions to maintain the correct concentration of minerals inside and outside of the membrane, and without this correct maintenance, severe symptoms and diseases can occur such as neuron degeneration and Alzheimer's disease.[9]
Mutations affecting GPI that reduce expression of CD59 and decay-accelerating factor on red blood cells result in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.[10] GPI mutation and consequent reduction in CD59 expression results from a cysteine to tyrosine missense mutation, which prevents disulfide bridge formation, ultimately disrupting tertiary protein structure and preventing proper GPI-CD59 complex binding.[11]
Viruses such as HIV, human cytomegalovirus and vaccinia incorporate host cell CD59 into their own viral envelope to prevent lysis by complement.[12] Additionally, CD59 has been investigated as a target for immunotherapy when treating certain cancers such as breast cancer. Researchers have found that once CD59 had been targeted, there is an upregulation in fas and caspase-3, creating an increase in apoptosis and tumor growth suppression in MCF-7 cells.[13]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000085063 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000068686 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CD59 molecule, complement regulatory protein".
- ^ a b Maio M, Brasoveanu LI, Coral S, Sigalotti L, Lamaj E, Gasparollo A, et al. (August 1998). "Structure, distribution, and functional role of protectin (CD59) in complement-susceptibility and in immunotherapy of human malignancies (Review)". International Journal of Oncology. 13 (2): 305–318. doi:10.3892/ijo.13.2.305. PMID 9664126.
- ^ Couves EC, Gardner S, Voisin TB, Bickel JK, Stansfeld PJ, Tate EW, et al. (February 2023). "Structural basis for membrane attack complex inhibition by CD59". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 890. Bibcode:2023NatCo..14..890C. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-36441-z. PMC 9935631. PMID 36797260.
- ^ Huang Y, Qiao F, Abagyan R, Hazard S, Tomlinson S (September 2006). "Defining the CD59-C9 binding interaction". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (37): 27398–27404. doi:10.1074/jbc.M603690200. PMID 16844690.
- ^ Farkas I, Baranyi L, Ishikawa Y, Okada N, Bohata C, Budai D, et al. (March 2002). "CD59 blocks not only the insertion of C9 into MAC but inhibits ion channel formation by homologous C5b-8 as well as C5b-9". The Journal of Physiology. 539 (Pt 2): 537–545. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013381. PMC 2290142. PMID 11882685.
- ^ Parker C, Omine M, Richards S, Nishimura J, Bessler M, Ware R, et al. (December 2005). "Diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria". Blood. 106 (12): 3699–3709. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-04-1717. PMC 1895106. PMID 16051736.
- ^ Nevo Y, Ben-Zeev B, Tabib A, Straussberg R, Anikster Y, Shorer Z, et al. (January 2013). "CD59 deficiency is associated with chronic hemolysis and childhood relapsing immune-mediated polyneuropathy". Blood. 121 (1): 129–135. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-07-441857. PMID 23149847. S2CID 19110288.
- ^ Bohana-Kashtan O, Ziporen L, Donin N, Kraus S, Fishelson Z (July 2004). "Cell signals transduced by complement". Molecular Immunology. 41 (6–7): 583–597. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2004.04.007. PMID 15219997.
- ^ Li B, Chu X, Gao M, Xu Y (2011). "The effects of CD59 gene as a target gene on breast cancer cells". Cellular Immunology. 272 (1): 61–70. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.09.006. PMID 22000275.
Further reading
- Tandon N, Morgan BP, Weetman AP (February 1992). "Expression and function of membrane attack complex inhibitory proteins on thyroid follicular cells". Immunology. 75 (2): 372–377. PMC 1384722. PMID 1372592.
- Holmes CH, Simpson KL, Okada H, Okada N, Wainwright SD, Purcell DF, et al. (June 1992). "Complement regulatory proteins at the feto-maternal interface during human placental development: distribution of CD59 by comparison with membrane cofactor protein (CD46) and decay accelerating factor (CD55)". European Journal of Immunology. 22 (6): 1579–1585. doi:10.1002/eji.1830220635. PMID 1376264. S2CID 25836496.
- Ninomiya H, Sims PJ (July 1992). "The human complement regulatory protein CD59 binds to the alpha-chain of C8 and to the "b"domain of C9". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 267 (19): 13675–13680. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)42266-1. PMID 1377690.
- Petranka JG, Fleenor DE, Sykes K, Kaufman RE, Rosse WF (September 1992). "Structure of the CD59-encoding gene: further evidence of a relationship to murine lymphocyte antigen Ly-6 protein". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 89 (17): 7876–7879. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.7876P. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.17.7876. PMC 49817. PMID 1381503.
- Motoyama N, Okada N, Yamashina M, Okada H (October 1992). "Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria due to hereditary nucleotide deletion in the HRF20 (CD59) gene". European Journal of Immunology. 22 (10): 2669–2673. doi:10.1002/eji.1830221029. PMID 1382994. S2CID 23829471.
- Rooney IA, Morgan BP (August 1992). "Characterization of the membrane attack complex inhibitory protein CD59 antigen on human amniotic cells and in amniotic fluid". Immunology. 76 (4): 541–547. PMC 1421564. PMID 1383132.
- Tone M, Walsh LA, Waldmann H (October 1992). "Gene structure of human CD59 and demonstration that discrete mRNAs are generated by alternative polyadenylation". Journal of Molecular Biology. 227 (3): 971–976. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(92)90239-G. PMID 1383553.
- Philbrick WM, Palfree RG, Maher SE, Bridgett MM, Sirlin S, Bothwell AL (January 1990). "The CD59 antigen is a structural homologue of murine Ly-6 antigens but lacks interferon inducibility". European Journal of Immunology. 20 (1): 87–92. doi:10.1002/eji.1830200113. PMID 1689664. S2CID 23636682.
- Sawada R, Ohashi K, Anaguchi H, Okazaki H, Hattori M, Minato N, et al. (April 1990). "Isolation and expression of the full-length cDNA encoding CD59 antigen of human lymphocytes". DNA and Cell Biology. 9 (3): 213–220. doi:10.1089/dna.1990.9.213. PMID 1692709.
- Yamashina M, Ueda E, Kinoshita T, Takami T, Ojima A, Ono H, et al. (October 1990). "Inherited complete deficiency of 20-kilodalton homologous restriction factor (CD59) as a cause of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria". The New England Journal of Medicine. 323 (17): 1184–1189. doi:10.1056/NEJM199010253231707. PMID 1699124.
- Rooney IA, Morgan BP (November 1990). "Protection of human amniotic epithelial cells (HAEC) from complement-mediated lysis: expression on the cells of three complement inhibitory membrane proteins". Immunology. 71 (3): 308–311. PMC 1384423. PMID 1702747.
- Watts MJ, Dankert JR, Morgan EP (January 1990). "Isolation and characterization of a membrane-attack-complex-inhibiting protein present in human serum and other biological fluids". The Biochemical Journal. 265 (2): 471–477. doi:10.1042/bj2650471. PMC 1136908. PMID 2302178.
- Okada H, Nagami Y, Takahashi K, Okada N, Hideshima T, Takizawa H, et al. (August 1989). "20 KDa homologous restriction factor of complement resembles T cell activating protein". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 162 (3): 1553–1559. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(89)90852-8. PMID 2475111.
- Davies A, Simmons DL, Hale G, Harrison RA, Tighe H, Lachmann PJ, et al. (September 1989). "CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 170 (3): 637–654. doi:10.1084/jem.170.3.637. PMC 2189447. PMID 2475570.
- Sawada R, Ohashi K, Okano K, Hattori M, Minato N, Naruto M (August 1989). "Complementary DNA sequence and deduced peptide sequence for CD59/MEM-43 antigen, the human homologue of murine lymphocyte antigen Ly-6C". Nucleic Acids Research. 17 (16): 6728. doi:10.1093/nar/17.16.6728. PMC 318369. PMID 2476718.
- Sugita Y, Tobe T, Oda E, Tomita M, Yasukawa K, Yamaji N, et al. (October 1989). "Molecular cloning and characterization of MACIF, an inhibitor of membrane channel formation of complement". Journal of Biochemistry. 106 (4): 555–557. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122893. PMID 2606909.
- Bora NS, Gobleman CL, Atkinson JP, Pepose JS, Kaplan HJ (December 1993). "Differential expression of the complement regulatory proteins in the human eye". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 34 (13): 3579–3584. PMID 7505007.
- Kieffer B, Driscoll PC, Campbell ID, Willis AC, van der Merwe PA, Davis SJ (April 1994). "Three-dimensional solution structure of the extracellular region of the complement regulatory protein CD59, a new cell-surface protein domain related to snake venom neurotoxins". Biochemistry. 33 (15): 4471–4482. doi:10.1021/bi00181a006. PMID 7512825.
- Kennedy SP, Rollins SA, Burton WV, Sims PJ, Bothwell AL, Squinto SP, et al. (May 1994). "Protection of porcine aortic endothelial cells from complement-mediated cell lysis and activation by recombinant human CD59". Transplantation. 57 (10): 1494–1501. doi:10.1097/00007890-199405000-00017. PMID 7515200.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to CD59.
PDB gallery
-
1cdq: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 -
1cdr: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 -
1cds: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 -
1erg: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS -
1erh: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS -
2ofs: Crystal structure of human CD59 |


 1cdq: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59
1cdq: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 1cdr: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59
1cdr: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 1cds: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59
1cds: STRUCTURE OF A SOLUBLE, GLYCOSYLATED FORM OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN CD59 1erg: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS
1erg: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS 1erh: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS
1erh: THREE-DIMENSIONAL SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR REGION OF THE COMPLEMENT REGULATORY PROTEIN, CD59, A NEW CELL SURFACE PROTEIN DOMAIN RELATED TO NEUROTOXINS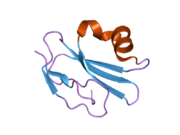 2ofs: Crystal structure of human CD59
2ofs: Crystal structure of human CD59
























